Exemplification for foundation subjects
Religious education exemplification standards file level 4
Pupil's profile
Pupil B is an inquisitive student who enjoys asking questions about religion and exploring ideas in group work. She is a Muslim, which helps her to understand and appreciate the significance of religion. Her written work is not as strong as her oral work, partly because English is her second language.
Evidence groups
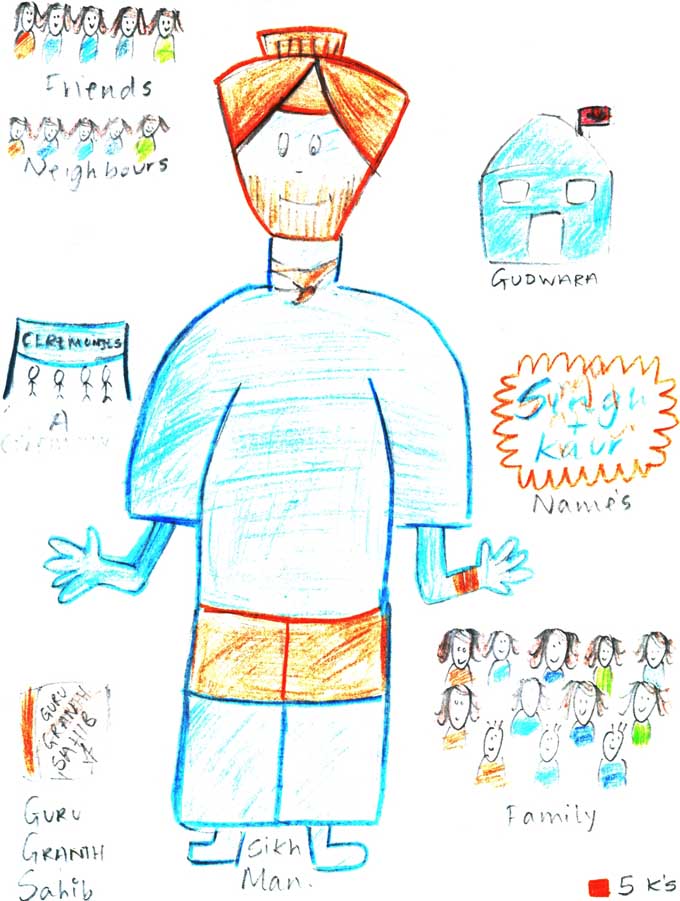
How do we express our identity? A focus on Sikhism
Context
During a unit of work on identity, diversity and belonging, pupils explored how identities are expressed by producing two collages. In the first collage, pupils used their knowledge and understanding of Sikhism from previous lessons to illustrate how a Sikh might express his identity. In the second collage they expressed their own identity. Pupils explained the choices they made in their collages in a written piece of work.
Pupil's work
Next steps
To progress, Pupil B needs to:
explore the similarities and differences within a religion, for example by meeting, virtually or physically, members of a religion who can explain how they may practise their faith in different ways
explain her answers to questions raised by the study of religion and provide evidence to support them.
How can we compare and contrast Hindu and Muslim beliefs about God?
Context
Pupils explored Hindu and Muslim beliefs about God by learning about the story of Svetaketu from the Upanishads and Surah 112 from the Qur'an. In the story of Svetaketu the presence of the divine in all things is compared with the presence of salt dissolved in water. In the Qur'an different aspects of the nature of God are described.
After watching a role play of the story and discussing what they saw, they did a reciprocal reading activity with each pupil taking a different role such as questioner or summariser to help them analyse the Qur'anic texts. They then used a database of statements by young people to compare Hindu and Muslim beliefs and suggest a meaning for each text. As a class, they discussed how the nature of God is portrayed. Using differentiated levels of support, such as a word-bank and writing frames, pupils then summarised their ideas in a written piece of work.
Pupil's work
Assessment Commentary
Pupil B can identify the similarities and differences between two religions' teaching about the divine and suggest meanings for forms of religious expression.
Thinking about religion and belief:
Pupil B has shown that she can describe similarities between religions by correctly asserting that both texts express common beliefs about God and illustrating that point: 'they both believe that God is one, he hasn't been created and always has existed'. Pupil B's conversation with the teacher provides further evidence that she can describe similarities between Hindu and Muslim worship. She discusses the use of prayer beads to help the worshipper focus on God. She has also described connections between questions, sources and beliefs.
Enquiring, investigating and interpreting:
Pupil B has suggested meanings for different forms of religious expression, using appropriate vocabulary. She has shown she understands that the story in the Upanishads and from the Qur'anic texts both teach aspects of the nature of God: '… the [story of] Svetaketu shows that God is eternal and everlasting. In the same way, Muslims believe that Allah is eternal. This is shown by Surah 112 - Purity of Faith and Art Thou That.' She has used terms such as 'eternal', 'creator', 'absolute' and 'God is the essence to all things' appropriately.
Next steps
To progress, Pupil B needs to:
explain how her evidence, such as the quotation from a Holy Book, supports her point, such as an assertion that both Muslims and Hindus believe that God is the creator of the universe
explain the impact of sources from text and tradition on Hindu and Muslim belief
explain how and why Hindus use murtis - an image or deity - as a focus of worship of God whereas Muslims do not allow any representation of God.
What's my ideal state?
Context
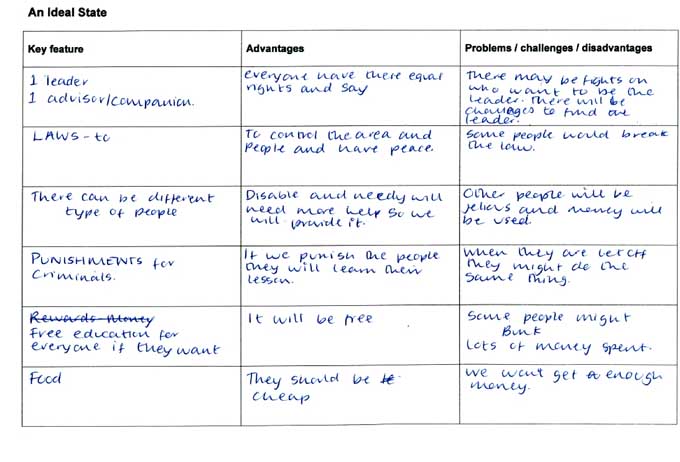
Pupils explored the concept of an ideal state by learning about the founding of the Ummah by the Prophet Muhammad. As a class, they shared ideas about the viability of an ideal state and what they thought its key features would be. They discussed the advantages and disadvantages of each feature and recorded their ideas. Pupils then compared their ideal state with features of the Muslim Ummah.
Pupil's work
Assessment Commentary
Pupil B can describe the impact of beliefs on individuals and communities and apply her ideas and reflections in the context of their own and others' lives.
Thinking about religion and belief:
She has described the impact of beliefs on a community. In the piece of prose she has compared some features of her own ideal state with those of the Ummah. She recognises that belief in the Ummah makes a difference in the way individuals and communities behave: '…one key difference between my ideal state and the Ummah is they don't have a leader the people can vote [for] and say what they want by voting. And they can say if they want to change anything.'
Reflecting, evaluating and communicating:
Pupil B has recorded her ideas and reflections on an ideal state and described how different features might affect her own and other people's lives. She has described the potential advantages and disadvantages. For one of the key features, punishments for criminals, she has also suggested what might happen as a result of others' attitudes and actions. She has written 'if we punish the people they will learn their lesson' [however] 'when they are let off, they might do the same thing.'
Next steps
To progress, Pupil B needs to:
develop her ability to explain her ideas using relevant sources and evidence
develop arguments about religious viewpoints and beliefs.
What similarities and differences can we find within different branches of Islam?
Context
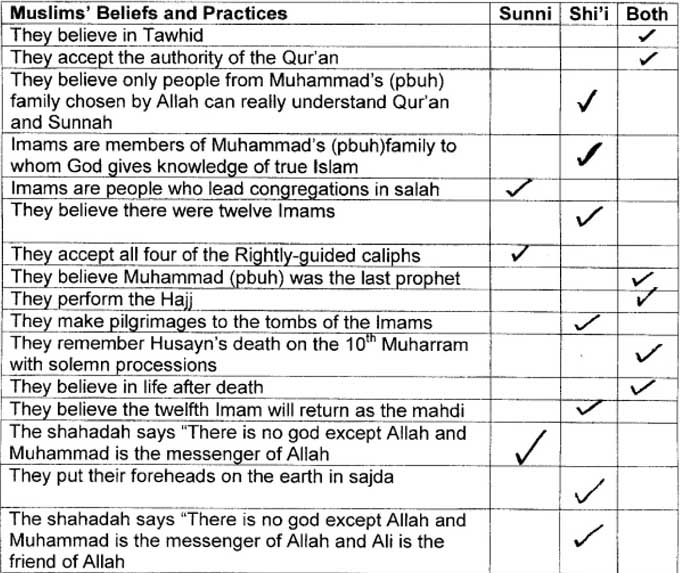
Pupils investigated similarities and differences within Islam. They learnt about the features of Sunni and Shi'a Islam from a number of written and online sources. The teacher decided to focus on Twelver Shi'a belief and practice rather than deal with the diversity within Shi'a Islam at this stage. Pupils were given a list of some key Muslim beliefs and practices to help them identify the similarities and differences. As a class, they repeated this activity using an interactive whiteboard.
Pupil's work
Assessment Commentary
Pupil B used a number of written and online sources to identify the similarities and differences within Islam.
Thinking about religion and belief:
Pupil B selected the appropriate column for each of the 16 statements about Islam. This has shown she can identify the similarities and differences within a religion. She was able to demonstrate a higher level of achievement by taking part in a class discussion. Through these oral contributions she was able to justify the decisions she made with specific descriptions of the diversity within Islam and debate with others who disagreed with her opinion.
Next steps
To progress Pupil B needs to:
explain the reasons for similarities and differences and how they might affect Muslims' lives.
How do I feel about the fact that there are different types of Muslims?
Context
Each pupil chose a question to discuss on Islam and in small groups placed their questions on a sheet of paper. Each group then decided which question would produce the most interesting answer. Following group discussion, pupils presented their responses orally or in writing.
Pupil's work
Assessment Commentary
Pupil B's group chose to discuss different types of Muslims. She developed her own ideas and exchanged and debated these ideas with those in her group. In her written work, she expressed a personal view, which took account of the group discussion.
Enquiring, investigating and interpreting:
Pupil B has suggested some answers to a question about the differences within her own religion. In her written work, she starts from a negative position: 'I don't really like it that we have Sunni and Shi'a Muslims' and justifies this by writing 'it would be bad if we met Shi'a Muslims and we started arguing about whose teaching is right'. She has appreciated that diversity within religion sometimes causes conflict. Gradually she suggests more positive answers: 'I know that we agree about the important things like Tawhid, the authority of the Qur'an and our prophet (Muhammad).' She has appreciated that there are similarities between the Sunni and Shi'a branches of Islam. Her final answer is positive: 'I don't mind because they are just trying to find ways to go to heaven like all Muslims in different ways.' This shows she has recognised a common goal for all Muslims.
Next steps
To progress, Pupil B needs to:
find relevant sources and evidence to support her assertions about Sunni and Shi'a beliefs and practices.
Overall assessment judgement
Religious education exemplification standards level 4
Overall, Pupil B is working at level 4.
Thinking about religion and belief:
The work in this collection shows Pupil B's progression from making links between features of religions to constructing descriptions that comment on features such as stories and beliefs. She has recognised similarities and differences within and between religions.
Enquiring, investigating and interpreting:
Pupil B was motivated by the challenge of researching aspects of identity with a view to creating a piece of artwork. She worked independently with a range of sources to tackle some challenging questions about her own tradition and suggested her own answers. During small group discussions, she was able to suggest meanings for a range of forms of religious expression. Her religious vocabulary is well developed.
Reflecting, evaluating and communicating:
Pupil B has written thoughtfully about the impact of sources of inspiration on her own and others' lives. She has used her own experiences and those of her family members to enhance her descriptions. By scaffolding the written response, the teacher was able to provide Pupil B with the opportunity to demonstrate her ability to apply religious ideas to her own life and to consider the consequences of certain ideas and actions.
The extracts of pupil work below are a reminder of some of the evidence used to make these judgements.


_thumb_tcm8-16955.jpg)
_thumb_tcm8-16956.jpg)


_medium_tcm8-17422.jpg)
_medium_tcm8-17423.jpg)









Assessment Commentary
Pupil B can describe the impact of a religious practice on herself and others. She can gather, select and organise questions and ideas.
Thinking about religion and belief:
She has described the impact of wearing the Muslim headscarf (hijab) on her own and other people's lives. She has also written about how she feels: 'It makes me confident to talk to others so that they don't look at my [hair] and judge. It also makes me feel brave …when I had to go to secondary I wasn't nervous like other girls I was actually happy because people looked at me and saw that I was a Muslim and I respect my religion.'
Enquiring, investigating and interpreting:
She has gathered, selected and organised ideas about religion and belief successfully. For her two collages, she considered what she learnt about Islam and Sikhism in previous lessons and chose appropriate material to include. She has presented her ideas clearly in both collages. In her written work she has suggested meanings for a form of religious expression, using an appropriate religious concept: 'The bracelet that my grandparents bought for me. It isn't just a bracelet, it is a bracelet from Hajj and Hajj is a place of worship. A place that you can be close to Allah … .'
Reflecting, evaluating and communicating:
She has described Hajj as a source of inspiration that makes a difference to her own life and the lives of others, which is also represented in the collage. Other forms of inspiration mentioned and represented in this way include the flag of Bangladesh, learning, the Qur'an and her family and friends.